Among the many technological breakthroughs of the 21st century, none have been met with as much optimism as blockchain. Created in 2009 by an anonymous user/users going by the pseudonym of Satoshi Nakamoto, blockchain has been viewed by many as a disruptive technology. Blockchain is a shared ledger which records and tracks transactions. The data on this ledger cannot be modified or changed and is completely transparent and immutable. Furthermore, the information can only be viewed by authorized network members and is free from the interference of the public. A blockchain can store various data relating to transactions, order history, account history, etc (IBM, n.d.).
Trustless Trust?
Blockchain’s entire existence revolves around eliminating third parties. A considerable amount of trust is involved when making any kind of transaction. Rather than trusting a third party, blockchain’s premise is to make people trust technology based on mathematical formulas which are objective and verifiable, leading to a situation of trustless trust. This is the main cause of concern and the key reason for scepticism of this technology.
Scepticism
Sceptics argue that due to the way blockchain operates, people will be putting blind faith into technology. No matter how secure a programme claims to be, a bug in the code could lead to the entire programme crashing. Furthermore, if the database gets hacked, the data of millions of people and institutions would be stolen leading to a situation of monumental priority.
Building blocks for the future
As more and more businesses and individuals worry about privacy and data security, blockchain may possibly hold the key to address these issues.
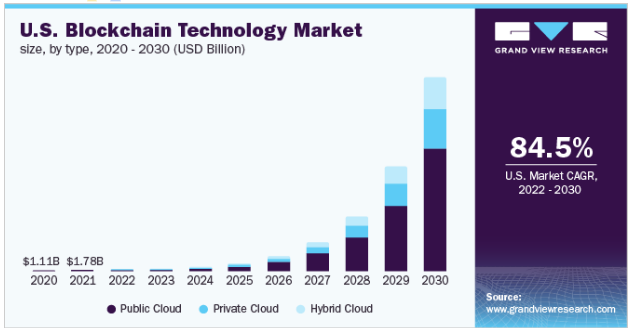
In the United States alone, the blockchain market was valued at US$5.92 billion in 2021 and is expected to grow immensely by 2030 owing to a CAGR of 84.5% (Grand View Research, n.d.).
Furthermore, the National Informatics Centre of India has established a Centre of Excellence to help implement blockchain solutions in a quick and seamless manner across the country with the collaboration of the government, public and private sectors. This is important as 56% of Indian businesses plan to implement blockchain in their operations (Malhotra, 2022).
Blockchain technology is experiencing a massive popularity surge in the banking and finance sector, with 66% of banks expected to roll out solutions within the next 3 years (European Business Review, 2021).
An interesting trend taking place is the push to make blockchain more eco-friendly as the technology consumes energy, thereby fuelling carbon emissions. From carbon offsetting to POS models of operations, blockchain is fuelling the growth of renewable energy.
After El Salvador’s recognition of Bitcoin as legal tender, the Indian government has changed its entire stance on cryptocurrency. From initially planning to ban cryptocurrency altogether, in 2022, the RBI announced plans to create its very own digital bank currency called the CBDC which is set to release by 2023. Many more countries are expected to launch their national cryptocurrencies and use cryptocurrencies powered by blockchain to pay salaries and purchase goods and services.
Developers are also investigating the possibility of integrating blockchain into IoT applications and even into managing supply chains of products which require intensive monitoring (luxury products and medicines).
The final block
There are still questions being asked about the technology and many still view this breakthrough with caution owing to the recent controversies with NFTs and the cryptocurrency crash. Therefore, it would be beneficial for both businesses and consumers to explore and learn more about blockchain and its functionality with it potentially being a high-risk high-reward investment.
References:
- IBM. (n.d.). What is blockchain technology? Retrieved from IBM: https://www.ibm.com/uk-en/topics/what-is-blockchain
- Grand View Research. (n.d.). Blockchain Technology Market Size, Share & Trends Analysis Report By Type. Retrieved from Grand View Research: https://www.grandviewresearch.com/industry-analysis/blockchain-technology-market
- Malhotra, A. (2022, February 14). THE RISE OF BLOCKCHAIN IN INDIA AND ITS FUTURE. Retrieved from analyticinsight: https://www.analyticsinsight.net/the-rise-of-blockchain-in-india-and-its-future/
- European Business Review. (2021, November). Future of Blockchain: How Will It Revolutionize The World In 2022 & Beyond! Retrieved from European Business Review: https://www.europeanbusinessreview.com/future-of-blockchain-how-will-it-revolutionize-the-world-in-2022-beyond/




